3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a rapidly growing field with many new trends and developments. From bioprinting human tissue to creating large-scale structures, the possibilities of 3D printing are endless. Here is a deep-dive in some of the top trends in the industry: these trends are shaping the future of manufacturing and have the potential to revolutionize the way we create and produce products.
Contents
As you read through my posts on emerging tech, my hope is that they will spark your interest in the topic and inspire you to learn more on your own. I will provide you with an overview of the latest developments in the field and give you examples of how these technologies are being used in the real world. My goal is to give you a sense of the potential impact that these technologies will have on our society and economy, and encourage you to explore the topic further. To help you in your journey, I will suggest some useful resources like articles, websites and other materials that can help you to explore the subject more in-depth.
Bioprinting
Bioprinting is a technique that utilizes 3D printing technology to fabricate biological structures, including human tissue and organs.
3D printing has come a long way in recent years, and one of the most exciting developments in the field is the use of 3D printing technology to create biological structures, such as human tissue and organs. This technology, known as bioprinting, has the potential to revolutionize the medical field by providing new ways to treat and diagnose diseases, as well as helping in the development of new drugs.
Bioprinting works by using specialized 3D printers to create complex structures made up of living cells. These structures can be used to create things like skin, blood vessels, and even functional organs like hearts and livers. The process involves using a special bio-ink made up of living cells and a gel-like substance to “print” the structure layer by layer.
Multi-material printing
Multi-material printing is the ability to print with multiple materials in a single object, allowing for more complex and functional objects.
Multi-material printing is a type of 3D printing technology that allows for the simultaneous printing of multiple materials, such as different colors or flexible and rigid materials. This is accomplished by using multiple extruders or print heads, or by using a single extruder that can switch between different materials as it prints. Multi-material printing expands the range of applications for 3D printing by enabling the creation of more realistic and functional objects, and also allows for the printing of parts that require different properties in different areas. For example, a part that requires flexibility in one area and rigidity in another can be printed with both materials, making it more suitable for its intended application.
Large-scale printing
Large-scale 3D printing consists in the development of large-scale 3D printers capable of printing large objects such as buildings and infrastructure.
Large-scale printing, also known as industrial 3D printing, refers to the use of specialized equipment and materials to create large-scale objects using additive manufacturing techniques. This process involves the layering of materials, such as plastics, metals, and ceramics, to create a finished product. This technology has many applications in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and healthcare. It allows for the creation of complex geometries, reduction of material waste, and the ability to produce items on-demand. Industrial 3D printing can also be used for rapid prototyping and low-volume production of end-use parts.
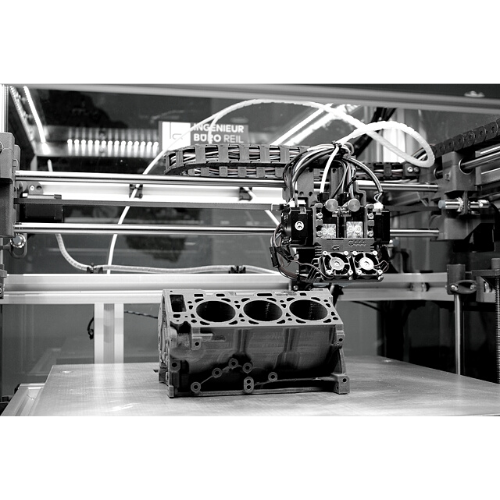
Metal printing
Advances in technology have made it possible to 3D print with metal materials, enabling the creation of complex metal structures and parts.
Metal printing is a type of 3D printing technology that uses metal powders or wires as the raw material to create 3D objects. The metal is melted or fused together layer by layer using various techniques such as: Directed Energy Deposition (DED), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Binder Jetting and Laser beam melting. Metal printing is widely used in aerospace, medical, and manufacturing industries, as it is able to produce high-density and high-strength parts that can withstand high temperatures and pressure. It’s also used in jewelry, art and prototyping. Metal printing is a complex process that requires specialized equipment and materials, and a high level of expertise to produce accurate and high-quality parts.
Materials research
Material research is the development of new materials, including composites and smart materials for use in 3D printing.
Materials research in the context of 3D printing refers to the study and development of new and advanced materials that can be used in additive manufacturing processes. This can include the optimization of existing materials for 3D printing, as well as the exploration of new materials with unique properties and capabilities. The goal of materials research in 3D printing is to improve the quality and performance of printed parts, increase the range of materials that can be used, and open up new possibilities for the use of 3D printing in various industries. It can include the study of material properties such as strength, flexibility, thermal conductivity, and biocompatibility, as well as the development of new printing techniques to enhance the processing of the materials.