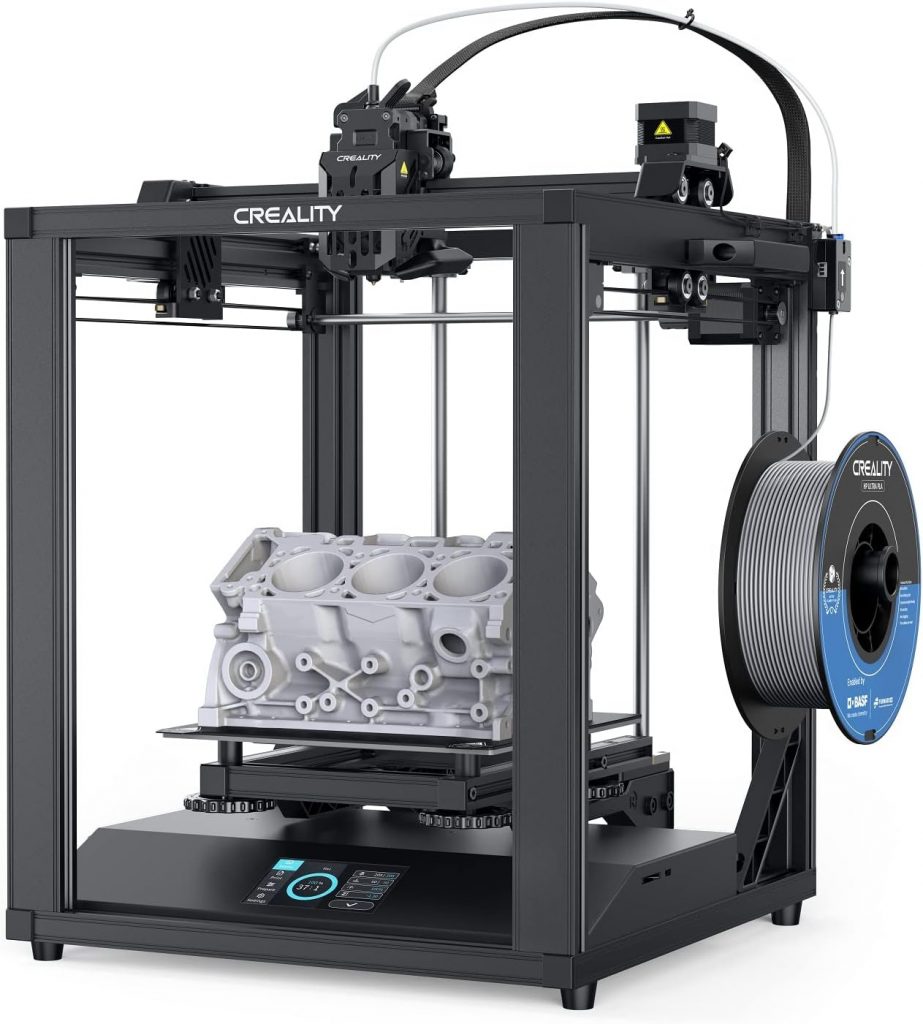
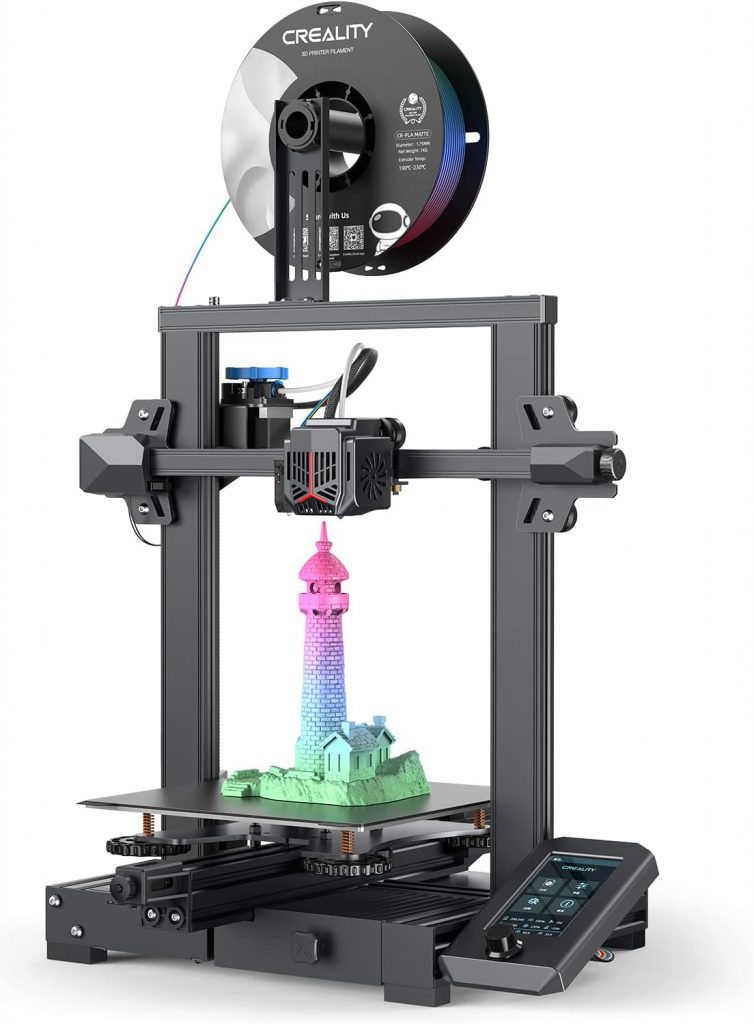
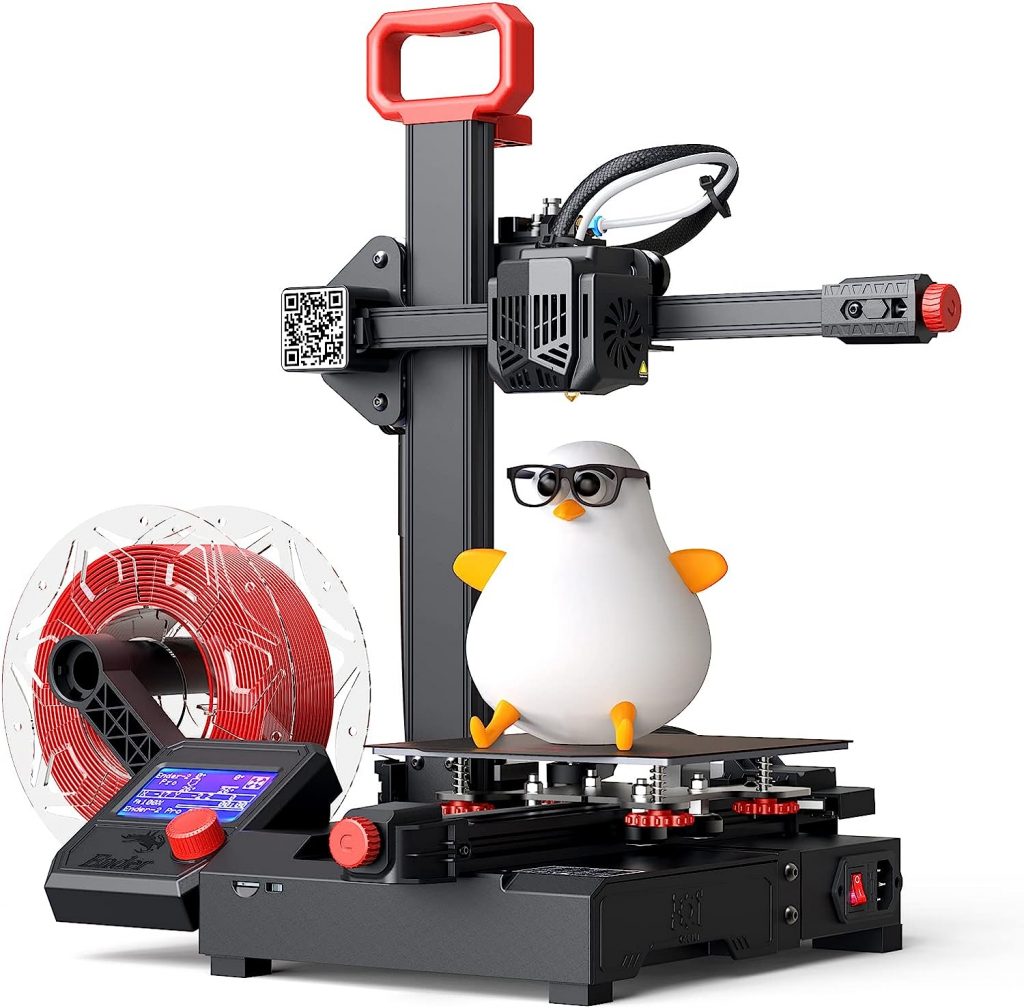
Among the different types of 3D printers available, filament 3D printers, also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) printers, are some of the most popular for both hobbyist and professional use. Choosing the right filament 3D printer can seem like a daunting task given the multitude of options available on the market. However, by considering several key criteria, you can simplify the decision-making process.
Examples of Filament 3D Printers
Contents
Filament 3D Printers
A filament in 3D printing is the material used to print objects. It’s usually a plastic-like material, such as PLA or ABS, that is heated up and extruded through a print head to create the 3D object layer by layer.
The most common types of 3D printing filaments are PLA (Polylactic Acid), ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), and PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol). Each type of filament has unique characteristics that make it suitable for different applications.
The filament is usually wound onto a spool and fed into the printer through a tube that leads to the extruder. The extruder heats up the filament, melting it into a liquid state, which is then pushed through a nozzle onto the print bed.
Most 3D printers use filament with a diameter of 1.75mm or 2.85mm. The 1.75mm filament is more common, but some printers use the larger 2.85mm size.
The temperature has a significant impact on how well the filament melts and extrudes. If the temperature is too low, the filament may not melt properly, leading to poor layer adhesion and print quality. If it’s too high, the filament may burn or become too liquid, causing stringing or blobbing. Each filament type has a recommended temperature range for optimal performance.
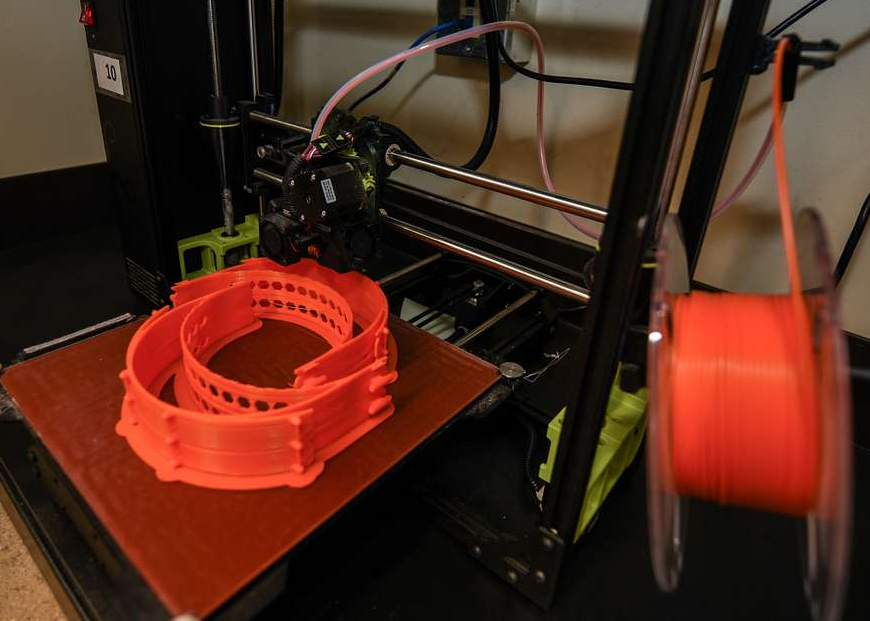
To use a filament 3D printer, you first need to design a 3D model of the object you want to print using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The printer then reads this model and creates the object by laying down thin layers of melted filament on top of each other. As each layer hardens, the printer moves the print bed (the surface on which the object is printed) downward and adds a new layer of filament on top.
Types of filament
There are many different types of filament that can be used with filament 3D printers, including PLA (polylactic acid), ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), PETG (glycol-modified PET), and nylon, among others. Each type of filament has its own unique properties and is suitable for different applications.
For example, PLA is a biodegradable plastic that is easy to print with, but may not be as strong as other materials, while ABS is a more durable plastic that is more resistant to temperature changes, but may be more difficult to print with.
There are many different types of filament that can be used with 3D printers, each with its own unique properties and characteristics. Here is a brief overview of some common filament types:
PLA (polylactic acid)
PLA is a biodegradable plastic made from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane. It is easy to print with, has a low melting temperature, and produces minimal odors when printing. However, it is not as strong as some other filament types and may not be suitable for high-stress applications.
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene)
ABS is a strong, durable plastic that is commonly used in the manufacturing industry. It is more resistant to temperature changes and has a higher melting temperature than PLA, but it can be more difficult to print with and produces more odors during printing.
PETG (glycol-modified PET)
PETG is a strong, flexible plastic that is resistant to impact and UV light. It is easy to print with and produces minimal odors, making it a popular choice for a wide range of applications.
Nylon
Nylon is a strong, flexible, and durable plastic that is resistant to wear and tear. It has a high melting temperature and can be difficult to print with, but is often used for high-strength parts and applications where flexibility is important.
PETT (polyethylene terephthalate)
PETT is a strong, stiff plastic that is resistant to impact and UV light. It has a low melting temperature and is easy to print with, making it a good choice for a wide range of applications.
TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane)
TPU is a flexible, rubber-like material that is resistant to wear and tear. It is often used for printing flexible parts, such as handles or grips, and has a low melting temperature.
PETE (polyethylene terephthalate)
PETE is a strong, stiff plastic that is resistant to impact and UV light. It has a low melting temperature and is easy to print with, making it a good choice for a wide range of applications.
Before you start
There are several steps you can take to choose a filament 3D printer:
Determine your needs
Before you start shopping for a 3D printer, it is important to determine your needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the print quality, speed, and material compatibility that are important to you, as well as your budget and any specific features you may need.
Research different models
Once you have a clear idea of what you are looking for, you can start researching different models of 3D printers. Look for reviews and comparisons of different models to get a sense of their features and capabilities.
Consider your budget
3D printers can range in price from under $100 to several thousand dollars. It is important to consider your budget when choosing a printer and to weigh the cost against the features and capabilities that are important to you.
Compare features and capabilities
Compare the features and capabilities of different 3D printers to determine which one is the best fit for your needs. Pay attention to details such as the print quality, build volume, and material compatibility.
Check the manufacturer’s reputation
It is important to choose a 3D printer from a reputable manufacturer that has a good track record for producing high-quality products and providing good customer support.
Consider post-purchase support
It is important to consider the level of post-purchase support that is offered by the manufacturer, in case you run into any issues or have questions about your printer.
Test out the printer
If possible, try to test out the printer before you buy it to get a sense of its performance and ease of use. You can often find 3D printers at maker spaces, hack-spaces, or other locations where they are available for use or demonstration.
Criteria for choosing a filament 3D printer
Assembly vs No Assembly
3D printers are available as assembled devices or to be assembled.
No assembly 3D printers are normally a better choice for a beginner but are normally providing less value for money. On the other hand disassembled 3D printers require additional effort since assembly is required in order to use them.
Print volume
3D printers are available in a wide variety of options, one important variable is the 3D print volume. The 3D print volume is the maximum size of the pieces you are able to print.
Most large 3D printers have a print volume around 25-35 cm in one of the dimensions and around 15-35 cm in the remaining two.
Nozzle diameter
The nozzle is the element that ejects the filament once it has been heated. The precision achieved in the parts depends on it. The precision indications are normally part of the 3D printer specs.
Printing speed
3D printers are not particularly fast in beginner models. A general recommendation is that the 3D printer is capable of exceeding 18-20 millimetres per second. Lower speeds would result in a poor user experience.
Positioning accuracy
This is where the three axes used for printing 3D parts (X, Y, Z) come into play. The guides used in each case must offer an accuracy of at least 0.02 mm in the first two and 0.004 mm in the third. The precision indications are normally part of the 3D printer specs, read them carefully.
Hot bed printing
The hot bed means that 3D print maintains a high temperature so that the part does not cool down when finished.
Supported file formats
In order to be able to use the creations that you can obtain for free on the Internet, the 3D device you purchase must support the use of STL and OBJ files, which are the standard with which this type of machine works.
Screen
A screen is not entirely indispensable, but having a screen that allows you to see how the printing process is proceeding is a good feature. It can be big or small, that is the least important, the fact is that it is there.
Connectivity
In addition to being able to connect the 3D printer to a computer, it is very important that it has other options for accessing work files. The key thing is that it has an SD card reader and it doesn’t hurt that it is also USB. Some entry-level models are also equipped with WiFi, allowing jobs to be sent from phones and tablets.
Light consumption
Basic models need about 130 W to run. This means that if you use the device for about 12 hours a day, you will spend about 75 cents per day.
Note: the cost of energy is very relevant. Given the current energy prices (August 2022), the cost for one day (24 hours of printing) is likely to be around 10 euros.
Size and weight
The size and weight of the 3D printer vary in each model and they are normally part of the 3D printer specs, read them carefully.
Selecting the right filament 3D printer can feel overwhelming due to the variety of options, but by focusing on these key criteria, you can make an informed decision that fits your needs and budget.