Bitcoin halving is a special event that gets people talking in the world of cryptocurrency. It happens roughly every four years and changes the amount of Bitcoin miners earn for their work. I’ve made a simple question and answer guide about Bitcoin halving. We’ll look at many parts of halving, from the simple ideas to the tricky ones. Together, we’ll learn how it works, its past, and how it changes the Bitcoin market.
So, if you’re an expert wanting more info, a miner wondering how it will affect you, or a beginner trying to understand what halving really means, I’ve tried to answer all questions in a way that’s easy to understand.
Contents
Basic concepts: what halving is and how it works
Bitcoin halving is a pre-planned event which takes place roughly every four years or upon the mining of every 210,000 blocks. During this halving process, the reward that Bitcoin miners receive for each new block mined is reduced by 50%. This event is essential within the Bitcoin ecosystem as it functions as a mechanism to control inflation.
The halving process in Bitcoin is programmed to occur after every 210,000 blocks have been mined, which equates to approximately every four years. This implies that the reward for mining a block is halved after these 210,000 blocks. This automatic mechanism is embedded within Bitcoin’s foundational code and takes place regardless of the level of transactions or activity on the Bitcoin network.
The Bitcoin block reward is the quantity of Bitcoin that a miner receives for successfully mining a new block on the Bitcoin blockchain. This reward serves as a motivation for miners to supply the necessary computational power to keep the network functional. Each time a halving event happens, this reward is reduced by half. For instance, post the last halving, the reward decreased from 12.5 to 6.25 Bitcoins per block.
Satoshi Nakamoto integrated the halving process into Bitcoin to control inflation and foster a sense of digital scarcity. The systematic reduction in block rewards, brought about by halving, guarantees that there will never be more than 21 million Bitcoins in existence. This design mirrors the mining of physical resources such as gold, wherein extracting new gold becomes incrementally more challenging over time.
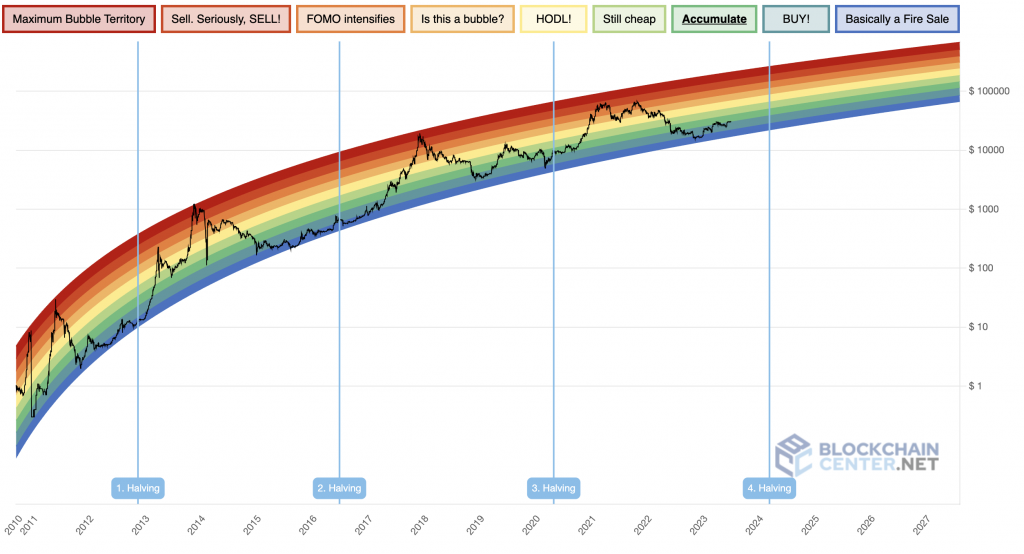
Basic concepts: dates and timing
The first halving
november 28, 2012
The reward per block went from 50 to 25 bitcoins.
The second halving
july 9, 2016
The reward per block was reduced from 25 to 12.5 Bitcoin.
The third halving
may 11, 2020
The reward per block was reduced from 12.5 to 6.25 Bitcoin.
The fourth halving
april 2024
The reward per block will be reduced from 6.25 to 3.125 Bitcoin.
The first halving of Bitcoin occurred on November 28, 2012. At that time, the block reward went from 50 Bitcoins per block to 25 Bitcoins. Since Bitcoin’s launch in 2009, this was the first halving event that took place.
The last halving of Bitcoin occurred on May 11, 2020. During this event, the reward per block went from 12.5 Bitcoin to 6.25 Bitcoin. The next halving is expected around 2024, depending on the pace of new block creation.
The next halving of Bitcoinis expected in April 2024, based on the current rate of block production, which occurs about every ten minutes. In this event, the reward for Bitcoin miners will be cut in half, from 6.25 to 3.125 Bitcoins per block.
Intermediate concepts: the consequences of halving
After a halving, the reward that miners receive for adding a new block to the blockchain is reduced by 50 percent. This means there are fewer new Bitcoins in circulation, which can affect Bitcoin supply and demand.
Halving reduces the rate of Bitcoin inflation. As the amount of new Bitcoin produced each day decreases, this reduces the supply of new Bitcoin. Given the same demand, this reduction in supply can lead to an increase in the price of Bitcoin, thus decreasing inflation.
For Bitcoin miners, a halving means that the reward they receive for mining each new block is halved. This can make mining less profitable, especially if electricity and equipment costs remain the same. Some miners may then decide to stop mining, which could lead to a reduction in the overall hash rate of the Bitcoin network.
Halving can affect the value of Bitcoin because of the law of supply and demand. Because halving reduces the supply of new Bitcoin, if demand remains the same or increases, the price of Bitcoin may increase. However, this depends on multiple factors and is not guaranteed.
Intermediate concepts: mining strategies
For Bitcoin miners, a halving means that the reward they receive for mining each new block is halved. This can make mining less profitable, especially if electricity and equipment costs remain the same. Some miners may then decide to stop mining, which could lead to a reduction in the overall hash rate of the Bitcoin network.
In the face of halving, Bitcoin miners could adopt several strategies. One of the most common is the accumulation of Bitcoin prior to halving. This is because the reward for blocking halves, so miners might try to mine as much as possible before the event. Others might choose to invest in more energy-efficient mining hardware to maintain profitability even with a reduced reward per block. Still others might choose to temporarily shut down their mining operations if the cost of energy exceeds the value of the reward per block after halving.
If the price of Bitcoin does not increase after halving, the profitability of miners may decrease significantly. As the reward per block halves, miners would need the price of Bitcoin to double to maintain the same level of profitability. If this did not happen, some miners might find it no longer profitable to participate in mining unless they have access to cheap electricity or very efficient mining hardware.
Advanced concepts: technical aspects
No, Bitcoin halving does not affect the speed at which new blocks are generated. The Bitcoin network is programmed to generate a new block approximately every 10 minutes, regardless of whether a halving has occurred or not. However, if a significant number of miners decide to quit after a halving due to reduced reward, this could temporarily affect the block generation speed until the mining difficulty is adjusted.
No, Bitcoin halving does not directly affect the energy required for Bitcoin mining. The energy used for Bitcoin mining is determined by the difficulty of mining, which in turn is influenced by the total number of miners in the network. If a halving leads many miners to quit because of the decrease in reward, the difficulty of mining might decrease and, therefore, the energy required for mining might also decrease. But this is an indirect effect.
Bitcoin halving can have an impact on network security. If the reward per block becomes too low, fewer miners may be incentivized to participate, which could potentially make the network more vulnerable to attacks. However, this scenario is largely theoretical, as transaction fees become a larger and larger part of the total reward for miners as rewards per block decrease.
Advanced concepts: economic aspects
Yes, Bitcoin halving is correlated with the concept of deflation. Halving reduces the supply of new Bitcoins entering circulation, which can lead to an increase in the value of each existing Bitcoin if demand remains the same or increases. This is similar to the concept of deflation, in which the value of money increases over time.
Bitcoin halving is an example of planned scarcity, a key concept in cryptocurrency economics. The idea is that by reducing the reward per block over time, the supply of new Bitcoin is reduced, which could lead to an increase in price if demand remains constant or increases. Historical evidence has shown that after each halving, the price of Bitcoin has increased significantly, although there have been lags and there is no guarantee that history will repeat itself.
Bitcoin halving has a significant impact on cryptocurrency market dynamics. First, it creates a reduction in the supply of new Bitcoin, which can lead to an increase in price if demand remains constant or increases. This can have trailing effects on other cryptocurrencies, as Bitcoin is often seen as an indicator of the cryptocurrency market as a whole. In addition, halving can lead to increased competition among miners as the reward for mining decreases. This can cause consolidation in the Bitcoin mining industry, with smaller operations becoming less profitable and potentially exiting the market.
Bitcoin halving is directly related to the concept of digital scarcity. Each halving reduces the amount of new Bitcoins that are created and distributed in the system, ensuring that the total supply never exceeds 21 million. This planned scarcity is a key element of Bitcoin’s value, making each Bitcoin more valuable because of its limited rarity.
Bitcoin’s halving, and in particular the idea of planned scarcity, is one of the main factors that has contributed to Bitcoin’s popularity. However, as per-block rewards continue to decline, the Bitcoin community and other cryptocurrencies will face long-term sustainability issues. Some possible solutions could include increasing transaction fees or changing the consensus protocol. Bitcoin’s halving could also influence the design of future cryptocurrencies and blockchain systems, which could seek to more effectively balance the incentive for miners and the long-term sustainability of the network.
Have more questions? Leave a comment below!
